In the digital age, data drives strategic decisions and competitive advantage for businesses. With reliance on analytics tools like Power BI increasing, prioritizing data governance and security is vital. This article explores the importance of enhancing data governance and security in Power BI, offering strategies for safeguarding data integrity.
The Significance of Data Governance and Security
Data governance refers to the framework, policies, and procedures put in place to ensure the consistent management, quality, integrity, and security of organizational data assets. Similarly, data security involves protecting data against unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction throughout its lifecycle. In the context of Power BI implementations, robust data governance and security measures are indispensable for several reasons:
- Maintaining Data Integrity: Ensuring the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data is paramount for making informed business decisions. Effective data governance practices help maintain data integrity by establishing standardized processes for data collection, storage, and analysis within Power BI.
- Mitigating Risks: Data breaches and cyber threats pose significant risks to organizations, potentially resulting in financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. Implementing robust security measures in Power BI environments is essential to mitigate these risks and safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access or malicious activities.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: With the enactment of stringent data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), organizations face increased pressure to comply with regulatory requirements concerning data privacy and security. Adhering to regulatory mandates necessitates the implementation of comprehensive data governance and security controls in Power BI deployments.
Strategies for Enhancing Governance and Security in Power BI
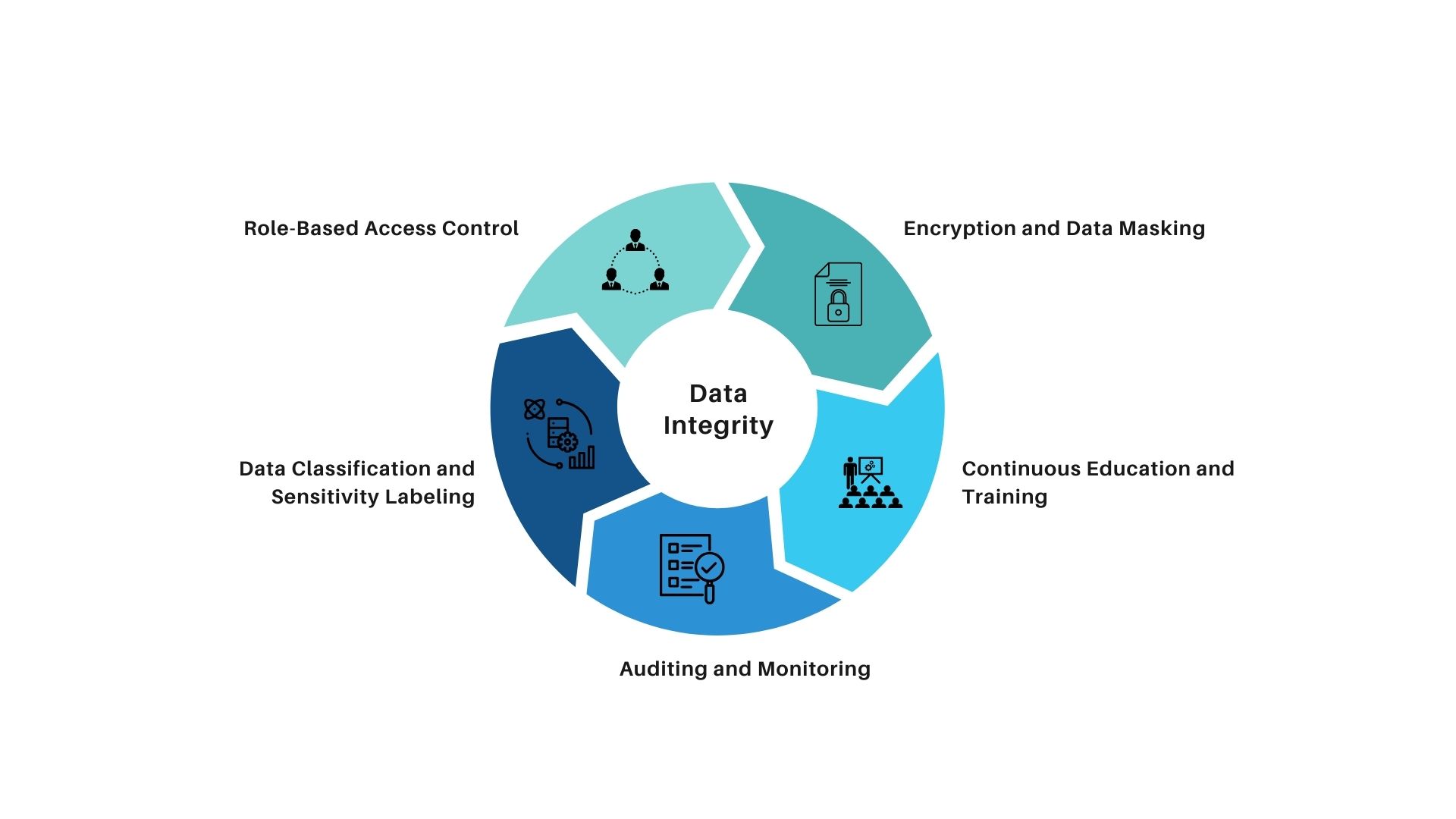
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement RBAC mechanisms in Power BI to restrict access to data and reports based on users’ roles and responsibilities within the organization. Define granular permissions to ensure that users only have access to the data necessary for their specific tasks while minimizing the risk of unauthorized data exposure.
- Data Classification and Sensitivity Labeling: Classify data based on its sensitivity level and apply appropriate sensitivity labels within Power BI to enforce data protection policies consistently. Utilize built-in features or third-party solutions to tag data with labels such as “Confidential,” “Internal Use Only,” or “Public” and configure access controls accordingly.
- Auditing and Monitoring: Enable auditing and monitoring capabilities in Power BI to track user activities, data access patterns, and changes made to reports and datasets. Regularly review audit logs and alerts to identify potential security incidents or compliance violations proactively and take appropriate remedial actions.
- Encryption and Data Masking: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest within Power BI to protect it from unauthorized interception or tampering. Additionally, leverage data masking techniques to obfuscate sensitive information displayed in reports and dashboards, ensuring that only authorized users can view unmasked data.
- Continuous Education and Training: Foster a culture of data security awareness among employees by providing comprehensive training programs on data governance best practices and security protocols. Educate users on the importance of adhering to data policies, recognizing potential security threats, and reporting incidents promptly to the relevant authorities.
In today’s data-driven landscape, prioritizing governance and security in Power BI is crucial. Taking proactive steps ensures data integrity, protects sensitive information, and meets regulatory standards. These strategies fortify Power BI security and inspire confidence in data management.
Industry Standards and Guidelines: Various industry organizations and regulatory bodies may offer guidelines and standards related to data integrity. For example, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) publishes standards such as ISO 8000 for data quality management.